-
Products
- Lab Instruments
- Lab Meters and Probes
- Chemistries, Reagents, and Standards
-
Online Analyzers
Ammonium Analysers Ammonia Monochloramine Chlorine Analyzers
- CL17sc
- CL10sc Amperometric
- 9184 sc Amperometric
- Ultra Low Range CL17sc Colorimetric Chlorine Analyser
EZ Series Analysers- Iron
- Aluminium
- Manganese
- Phosphate
- Chloride
- Cyanide
- Fluoride
- Sulphate
- Sulphide
- Arsenic
- Chromium
- Copper
- Nickel
- Zinc
- Ammonium
- Phenol
- Volatile Fatty Acids
- Alkalinity
- ATP
- Hardness
- Toxicity
- Sample Preconditioning
- Boron
- Colour
- Nitrate
- Nitrite
- Silica
- Hydrogen Peroxide
- EZ Series Reagents
- EZ Series Accessories
- EZ sc Series Inorganics
- EZ sc Series Metals
- EZ sc Series Nutrients
- Flow
-
Online Sensors and Controllers
Digital Controllers (Transmitters) Controllers (Analog)
- SC4500
- CA9300 Series Analog Transmitters
- Orbisphere 410/510 Carbon Dioxide
- Orbisphere 410/510 Oxygen
- Pro Series
pH & ORP Sensors- 12mm pH/ORP
- 8362 sc High Purity
- Combination pH/ORP
- Differential pH
- Digital Differential ORP
- Digital Differential pH
- LCP ORP
- LCP pH
- Sampling
- Multiparameter Online Panels
- Claros Water Intelligence System
- Test Kits & Strips
-
Microbiology
Prepared Media
- BARTS
- Liquid MPN
- MUG Tube
- Membrane Filtration
- Paddle Testers
- Presence-Absence
- Total Count Media
- Yeast and Mold
Dehydrated Media Kits Cryptosporidium & Giardia Analysis Legionella pneumophila Test Pseudomonas aeruginosa TestLabware- Accessories
- Funnels, Pumps & Manifolds
- Microbiology Filters
- Petri Dishes & Accessories
- Sampling Bags
- Vials, Tubes, Bottles & Racks
- Comparators
- Microbiology Accessories
- Microbiology Chemicals
- QC: Microbiology
- Quanti-Trays
- Sealer and Rubber Inserts
- UV Lamps
- Vessels
-
Lab Equipment and Supply
Apparatus
- Brushes
- Clamps, Rings & Stands
- Crucibles
- Crucibles & Casseroles
- Dispensers & Droppers
- Grab Samplers
- Oil and Grease
- Other Apparatus
- Pipet Aids
- Pipettes
- Racks
- Stir Bars
- Tubing
- Weighing Accessories
Instruments- Balances
- Hot Plates & Stirrers
- Microscopes
- Moisture Analysers
- Other Instruments
- Ovens & Incubators
- Thermometers
- Timers
- Vacuum Pump
- Automated Lab Systems
-
Environmental
Accessories Ambient Weather
- Kipp & Zonen Pyrgeometer
- Kipp & Zonen Scintillometer
- Lufft Ultrasonic Wind Sensor
- Lufft WS Series Smart Weather Sensor
- Lufft WS10 Series
Visibility and Present Weather Detection Hydrology Software Hydrology Water Discharge - Flow Road and Runway Sensors Solar Tracking and PV SoilingWater Level- OTT CBS Compact Bubbler Sensor
- OTT PLS Pressure Level Sensor
- OTT PLS(-C) Pressure Level Sensor with Conductivity
- OTT RLS Radar Level Sensor
- SUTRON Accubar Pressure Level Sensor
- SUTRON Constant Flow Bubbler
- SUTRON SDR Stage Discharge Recorder
Data Loggers and Telemetry- ADCON - Wireless Radio Communication / Telemetry
- Kipp & Zonen Data Logger
- SUTRON Antenna
- SUTRON SatLink 3 Logging Transmitter
- SUTRON XLINK 100 Logging Transmitter
- SUTRON XLINK 500 Logging Transmitter
- SUTRON XLite 9210 Datalogger
- SUTRON Xpert2 Datalogger
- Parameters
- Applications
- Industries
- Brands
- Service & Support
- News & Events
Hach Malaysia
Choose your country or region:
Europe
Americas
Asia - Australasia
- Australia
- Mainland China
- India
- Indonesia
- Japan
- Malaysia
- New Zealand
- Philippines
- Singapore
- South Korea
- Thailand (Thai)
- Taiwan
- Vietnam
Middle East - Africa
Chemistries 603-2779 2080
Turbidity
What is Turbidity?
Turbidity is the measure of the cloudiness or haziness of water.
More specifically, it's the measure of how light reflects off of suspended particles in water – specifically particles such as proteins, minerals, bacteria, algae, dirt and oil. The cloudier the water is, the higher its turbidity will be. It is not a measure of actual particles in the water.
A Basic Indicator of Water Quality
Turbidity has been recognized as a simple and basic indicator of water quality, and has been used for monitoring drinking water, including that produced by filtration for decades.
In almost all water supplies, high levels of suspended matter are unacceptable for aesthetic reasons and can interfere with chemical and biological tests.
What Causes Turbidity?
Turbidity is caused by particles in water that may not be visible on their own but can be seen with the naked eye when they’re clustered together.
Many of these particles come from matter that is commonly found in the environment, such as sediment, algae or small organisms like phytoplankton.
Particles in urban runoff and wastewater discharge can also contribute to increased turbidity of the source water.
Why Measure Turbidity?
There are many reasons to measure the turbidity of water but the primary one is to gauge its cleanliness—whether it’s source water, such as a lake in a state park or potable water in a municipal water distribution system.
Turbidity was originally used as a qualitative measurement in the early 1900s to classify the aesthetic quality of drinking water.
Today’s process is similar in that it relies on qualitative observations but involves instruments that use light-scattering technology for more specific readings.
Quality & aesthetics, health and compliance are just a few reasons why measuring turbidity matters.
Quality and Aesthetics
Water that looks cloudy isn’t just visually unappealing - it’s a hallmark sign of poor water quality, potentially correlating with bacterial contamination. If drinking water had high turbidity and was anything but crystal clear, it would be a red flag that the water might not be safe to drink.
High turbidity can also be an environmental concern. Although it is normal for some suspended particles to be present in lakes and rivers, the presence of too many particles in clusters can indicate that certain types of erosion are at play. Sedimentation, for example, can not only make lakes and rivers aesthetically unappealing, but it can also threaten ecosystems.
Higher levels of particulate matter prevent light from penetrating below the surface to fish and plants that live there. Those particles can also absorb more heat, making it impossible for some organisms to survive if the water temperature rises too much.
In contrast, bodies of water with low turbidity can indicate a healthy ecosystem with little erosion at play. The aesthetic benefits of low turbidity also benefit recreation and tourism industries, leading to a better quality of life overall.
Health Reasons
Water that’s rich in solid particles can offer a haven for bacteria and pathogens to grow. If left untreated, high turbidity can cause waterborne disease outbreaks. Today, the two most common threats in U.S. drinking water systems are Giardia lamblia cysts and Cryptosporidium parvum oocysts.
Such pathogens aren’t visible to the naked eye, but they can cause higher turbidity levels nonetheless. By taking a sample of drinking water and measuring its turbidity, it is possible to determine how many reflective particles are affecting it. Higher than normal levels indicate that the water may not be safe to drink and should be tested for the presence of bacteria.
Since turbidity levels change daily in drinking water sources such as the Great Lakes, regular monitoring allows plant operators to adjust their treatment operations accordingly.
Regulatory Compliance
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has several standards for water quality based on turbidity measurements. Water treatment plant operators are required to calibrate turbidimeters weekly or monthly, depending on the type of equipment in use.
Turbidity levels are measured in nephelometric turbidity units (NTU). According to the EPA, potable water must be kept at below 0.15 NTU for a stream coming out of an individual filtration line and below 0.30 NTU for the combined filter effluent of an entire water treatment plant.
Considering how sophisticated today’s turbidimeters are, the EPA’s calibration standards and NTU requirements may seem overly cautious. However, this presence of caution is essential considering that many water treatment plants rely on older equipment that might not be as accurate or efficient.
Featured Products to Measure Turbidity
TU5300sc/TU5400sc Online Laser Turbidimeters
The TU5 Series employs a patented optical design that sees more of your sample than any other turbidimeter, delivering the best low level precision and sensitivity while minimizing variability between measurements. Remove uncertainty of which measurement to trust between your lab and process instruments, thanks to identical 360° x 90° Detection Technology.
Learn MoreAccurate, color-independent suspended solids and turbidity measurements in accordance with DIN EN ISO. Due to a large measuring range for both turbidity and solids, the Solitax sc family offers a broad application spectrum and is ideal for drinking water, wastewater, surface water, and sludge treatment applications. A self-cleaning device prevents biological growth and interference of gas bubbles. Uses the infrared duo scattered light method.
Learn MoreSurface Scatter 7 sc High Range Turbidimeter
The Surface Scatter 7 sc High Range Turbidimeter offers superior performance across a measurement range of 0 to 9999 NTU. The Hach Surface Scatter 7 sc Turbidimeter (SS7) is the original non-contact turbidimeter. This design minimizes sensitivity loss due to high turbidity samples; in fluids with high loads of suspended solids the design makes sample cell cleaning and replacement unnecessary.
Learn MoreHach's TSS sc are digital special probes for determining turbidity and suspended solids in aqueous, and also aggressive, media, in accordance with DIN EN ISO. Made of highly polished stainless steel or titanium with a scratch resistant sapphire lens the TSS sc are ideal for high temperatures and pressures, for hygienically environments, or for corrosive media.
Learn MoreTU5 Series Laboratory Turbidimeters
The TU5200 is designed to deliver a revolutionary 360° x 90° Detection Technology, engineered to see more of your sample than any other turbidimeter. This unique technology is used in both the TU5 online and TU5 benchtop turbidimeters, allowing you for the first time to remove the uncertainty of which measurement to trust.
Learn MoreTL2350 Tungsten Lamp Turbidimeter, EPA, 0 - 10000 NTU
The new TL23 Series laboratory turbidimeters blend trusted technology and improved features to simplify testing in the most demanding wastewater and industrial applications.
Learn MoreTL2300 Tungsten Lamp Turbidimeter, EPA, 0 - 4000 NTU
Hach’s new TL23 lab turbidimeter brings a new face to the trusted legacy 2100N and 2100AN turbidimeters. It utilizes the same optic bloc while delivering an improved user experience with its intuitive interface, which ties perfectly to the rest of Hach’s laboratory instruments.
Learn MoreThe 2100Q portable turbidimeter provides convenient data logging. Up to 500 measurements are automatically stored in the instrument for easy access and backup. Stored information includes: date and time, operator ID, reading mode, sample ID, sample number, units, calibration time, calibration status, error messages, and the result.
Learn More
Which Applications and Processes Require Turbidity Monitoring?
Several industries require regular turbidity measurements in order to keep their day-to-day operations in check. While good water quality is essential, different processes reap additional benefits from measuring turbidity.
Drinking Water Treatment
While regulatory compliance is important for municipal drinking water and water treatment plants, measuring turbidity can also help keep the cost of operations down. Taking regular turbidity measurements can optimize filter performance by establishing efficient filter backwash cycles. And in the case of filter breakthrough, turbidity readings can indicate a breach of particles before it becomes a costly problem requiring an appropriate regulatory response.
Ultimately, turbidity measurements are an important part of quality control in water treatment plants. They help operators achieve their most important goal: Making water safe for consumers to drink.

Beverage Industry
Good water quality is vital in the beverage industry too, where the taste and texture of a drink are of utmost importance. For alcoholic beverages like wine and beer, flavor consistency and shelf life are at the heart of quality control. For bottled water and soft drinks, it’s easy for consumers to see when something is off—especially if turbidity is an issue.
Turbidity can vary dramatically depending on where water is sourced from in the beverage industry. Having turbidimeters operational ensures that manufacturers can monitor the quality of their water to see if it needs extra filtering or treatment. With consistent measuring, turbidity readings keep quality in check to ensure that water always meets high standards for beverage making.

Wastewater Treatment
A turbidimeter can reflect on the amount of suspended solids in water at different parts of the treatment process, whether it’s for compliance reporting or for process control in real time.
Turbidity measurements can help ensure that effluent meets quality standards in municipal wastewater.

How is Turbidity Measured?
There are three main ways for measuring turbidity and each has benefits for different industries.
Taking an indirect measurement with a Secchi disk or tube can be helpful for gauging turbidity relative to water clarity in a body of surface water such as a lake or river.
Turbidity sensors can be submerged in water to take more accurate readings using light-scattering techniques. Some turbidity meters, or turbidimeters, can take readings on a sample without touching the liquid directly.
Turbidimeters are the most versatile devices for measuring turbidity, since they can be used in a wide variety of settings. Turbidimeters usually employ a beam of light, called incident light, which scatters off of suspended particles in the sample being measured.
Nephelometry
The method of measuring scattered light at 90 degrees to the incident light beam is called nephelometry and the turbidimeter used for this type of measurement is a nephelometer. Nephelometers detect the amount of scattered light and compare it to a calibrated measurement standard that can be set by the user. If the water is more turbid, the light will scatter more. If it’s less turbid, the light will scatter less. Only nephelopmetric methods to measure turbidity are accepted for regulatory compliance and reporting in the US.
Different nephelometers and turbidimeters exist for different purposes, though their core principle of measurement remains the same—measure the portion of light scattered by the particles.

1) Process Turbidimeters for Continuous Monitoring
In drinking water and some wastewater treatment plants, it’s essential to monitor turbidity continuously to keep each step of the filtration process in check and avoid costly mishaps.
Process turbidimeters are simple, low-maintenance and accurate—perfect for an environment where they’re needed to provide readings at a moment’s notice.
2) Laboratory Benchtop Turbidimeters
Benchtop turbidimeters are perfect for measuring grab samples and conducting an array of tests on water from multiple sources.
They’re designed to be sensitive and precise for ultra-accurate measurements in controlled lab conditions.

3) Portable Turbidimeters for Remote Locations
Setting up a lab turbidimeter at a construction site or near a river after a storm would be an unnecessary hassle.
That's where portable turbidimeters are most useful. These handheld devices are durable, simple to use and able to conduct rapid tests in the field.
Turbidity Standards
Turbidimeters need to be calibrated according to standards set by manufacturers and regulatory organizations in order to ensure an accurate turbidity measurement. This is often done by using a liquid synthetic material called Formazin.
Formazin is the only recognized true primary standard for turbidimeter calibration. Newer standards, such as the StablCal ® Stabilized Formazin Turbidity Standards, build off of Formazin but have better stability.
StablCal standards, especially packaged in sealed vials, are ideal for calibrating turbidimeters in the field, because their higher stability and portability ensure a lab-grade quality reading even outside the lab.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do you use a turbidimeter?
All turbidimeters have different operating requirements, so it is important to check the instructions before use.
Nonetheless, most turbidimeters follow the same general procedure for benchtop or portable units:
- Uncap a clean vial, and fill it with the unfiltered water sample you wish to measure. Be sure to stir the sample by inverting the container before pouring it into the measurement cell to kick up particles that may have settled, but without creating air bubbles.
- Tighten the cap on the sample cell (or measurement cell) and hold it by the cap.
- Wipe away any excess liquid, dirt or finger markings from the cell with a soft lint-free cloth before measuring.
- Place the turbidimeter on a flat surface.
- Turn on the device.
- Set the automatic range.
- Select signal averaging.
- Put the cell into the measurement compartment of the turbidimeter.
- Close the compartment lid.
- Select the “Read” button, which should give you a measurement in NTU.
What is the normal range for turbidity in water?
Before disinfection, the turbidity of drinking water should be below 1 NTU, according to the World Health Organization’s standards .
If it’s above 1-2 NTU, the effectiveness of chlorination significantly decreases. In areas where fewer resources are available, the turbidity should be below 5 NTU.
What is the difference between turbidimeters and nephelometers?
Turbidimeters and nephelometers both measure the cloudiness of water. A nephelometer is a type of turbidimeter that measures the amount of light reflected off of particles at a 90-degree angle.
They are often used to test samples with suspected low turbidity, such as filtered water samples from a drinking water treatment plant. This type of turbidimeter is accepted for regulatory reporting according to EPA and ISO standards.
What is ultra-high turbidity measurement?
Ultra-high turbidity is when a sample is so turbid that traditional nephelometric light-scatter methods are not useful. At turbidities in excess of 2,000 NTU, there’s a decrease in nephelometric signal, and traditional turbidimeters cannot take an accurate reading of light scattered by the suspended solids.
Color can also influence turbidity measurement and the use of strictly nephelometric readings is not always an accurate way to gauge ultra-high turbidity in samples of surface water, wastewater, food products, cell cultures or oil in water, for example.
Fortunately, there are other techniques that can be used to measure ultra-high turbidity: transmitted, forward-scatter and back-scatter methods. Also known as ratio turbidimetry, these methods are used for many applications where ultra-high turbidity needs to be measured, such as monitoring the fat content in milk, for example.
What is the correlation between turbidity and total suspended solids (TSS)?
The foremost significant difference between these two parameters is that turbidity is method-derived, while TSS is an absolute parameter.
That means that TSS can be measured gravimetrically by evaporating all liquids, then weighing the solid residue and expressing concentration in milligrams per liter (mg/L). The difference is also reflected in dilution - the TSS of diluted samples is linear, while turbidity may not change linearly with the dilution of samples or standards.
A turbidimeter can estimate the TSS in a liquid. However, this only works if there is an established correlation between turbidity and the TSS of the sample, which may not be sustainable and can depend on various conditions.
What is the history of turbidity?
The first formal measure of water turbidity (circa 1900) was called the Jackson Candle Method (Figure 1). It was essentially a vertical glass tube mounted over a candle. The scale on the tube was calibrated using dilutions of a standard reference solution comprising 1,000 parts per million (ppm) of diatomaceous earth (silica) in distilled water.
The calibrated units of measure on the tube were called Jackson Turbidity Units (JTU). Sample water was poured into the tube until the distinct image of the candle flame was no longer visible to the human eye when viewed from straight above. The depth of water in the tube at that point corresponded to a distinct JTU reading on the scale of the tube.
Compared to today’s instruments and methods, that original method was a relatively crude measure of turbidity that could result in inconsistencies due to differences in the viewer’s eyesight and the candle used.
In 1926, Kingsbury, Clark, Williams and Post developed a new standard reference solution (formazin polymer) that was easier to formulate. It provided greater consistency than Jackson’s diatomaceous earth reference standard, which could vary according to the material source.
Formazin also does a good job of replicating the particulates and turbidity typically experienced in drinking water applications. One advantage of formazin is that, even though not all of the polymer chains are of an identical size, it produces a very regular response every time it is synthesized.
The formazin standard was a major step toward standardizing turbidity testing. It is still in use today, while other turbidimetry components — such as light sources and light detectors — have been refined to eliminate the variables of candlelight and human eyesight.
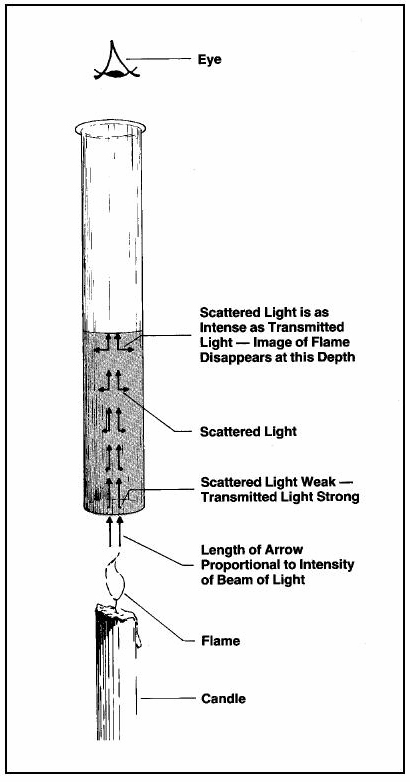
Figure 1.The original Jackson Candle Turbidimeter was based on the amount of light transmitted from a candle through a column of water.
PRODUCT SUPPORT
CUSTOMER SERVICE
RESOURCES
ABOUT US
Looking for our Hach US Site?
It appears that you are visiting Hach from the United States but the site you are currently visiting is for Malaysia.
Would you like to visit the Hach US site instead?



